Are you scouring the internet for 'phytochemical content of coffee substitute beverage biology essay'? You will find the answers here.
Table of contents
- Phytochemical content of coffee substitute beverage biology essay in 2021
- Applications of compounds from coffee processing by-products
- Health effects of coffee: mechanism unraveled
- Which country has the lowest rate of per capita caffeine consumption?
- Google scholar
- How did the term cappuccino originate
- Is coffee carbohydrate
- Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks
Phytochemical content of coffee substitute beverage biology essay in 2021
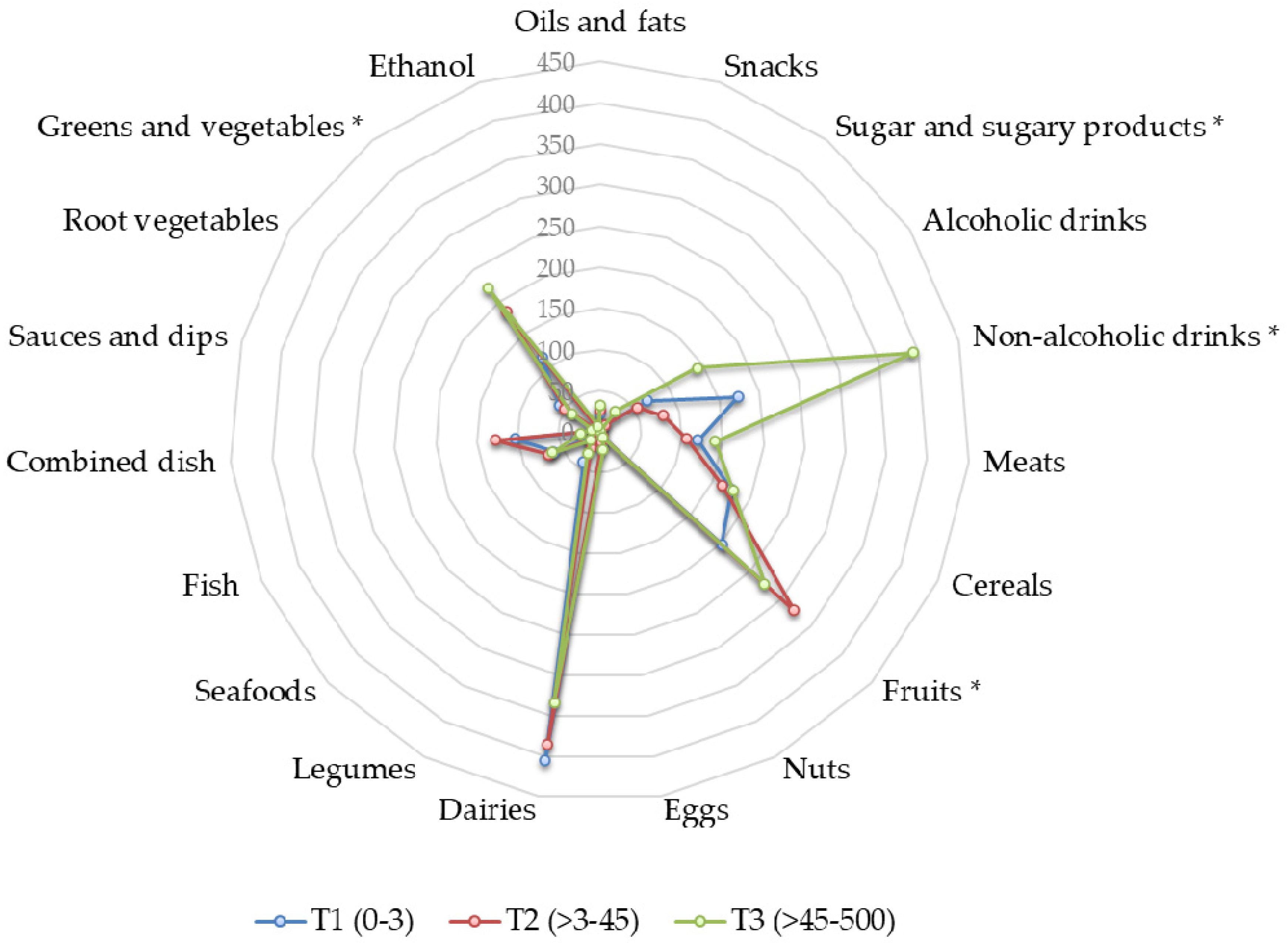 This image representes phytochemical content of coffee substitute beverage biology essay.
This image representes phytochemical content of coffee substitute beverage biology essay.
Applications of compounds from coffee processing by-products
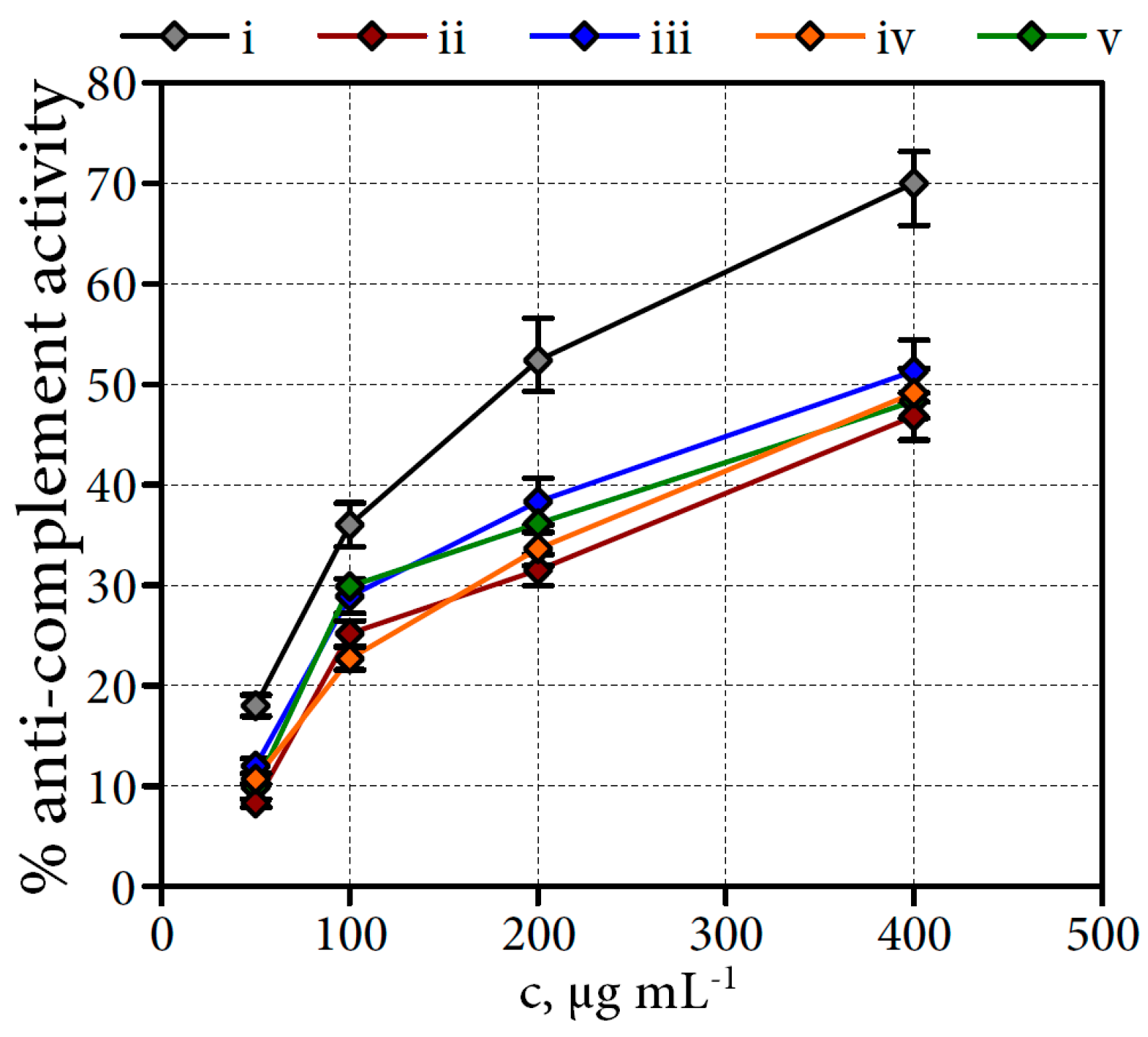 This picture representes Applications of compounds from coffee processing by-products.
This picture representes Applications of compounds from coffee processing by-products.
Health effects of coffee: mechanism unraveled
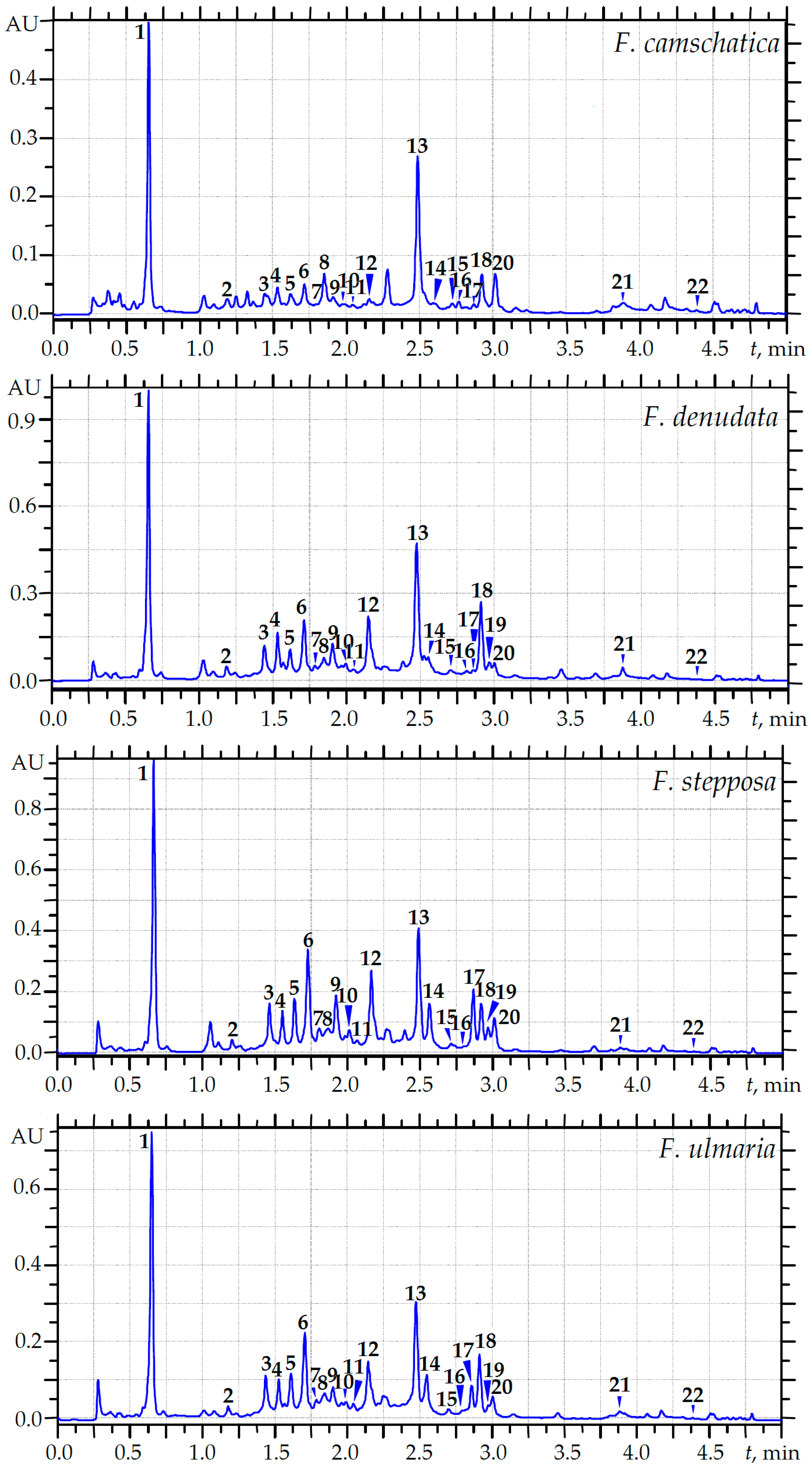
 This image demonstrates Health effects of coffee: mechanism unraveled.
This image demonstrates Health effects of coffee: mechanism unraveled.
Which country has the lowest rate of per capita caffeine consumption?
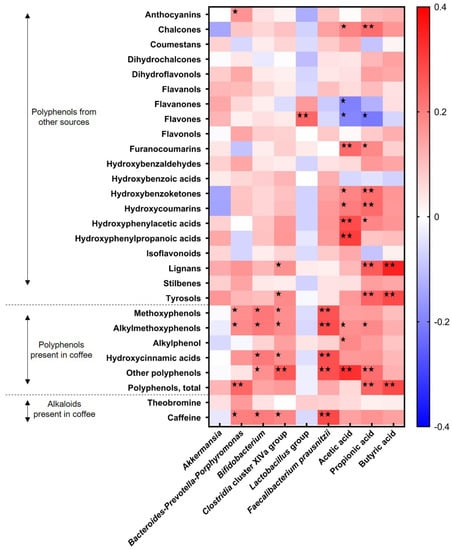
 This image representes Which country has the lowest rate of per capita caffeine consumption?.
This image representes Which country has the lowest rate of per capita caffeine consumption?.
Google scholar
 This picture demonstrates Google scholar.
This picture demonstrates Google scholar.
How did the term cappuccino originate
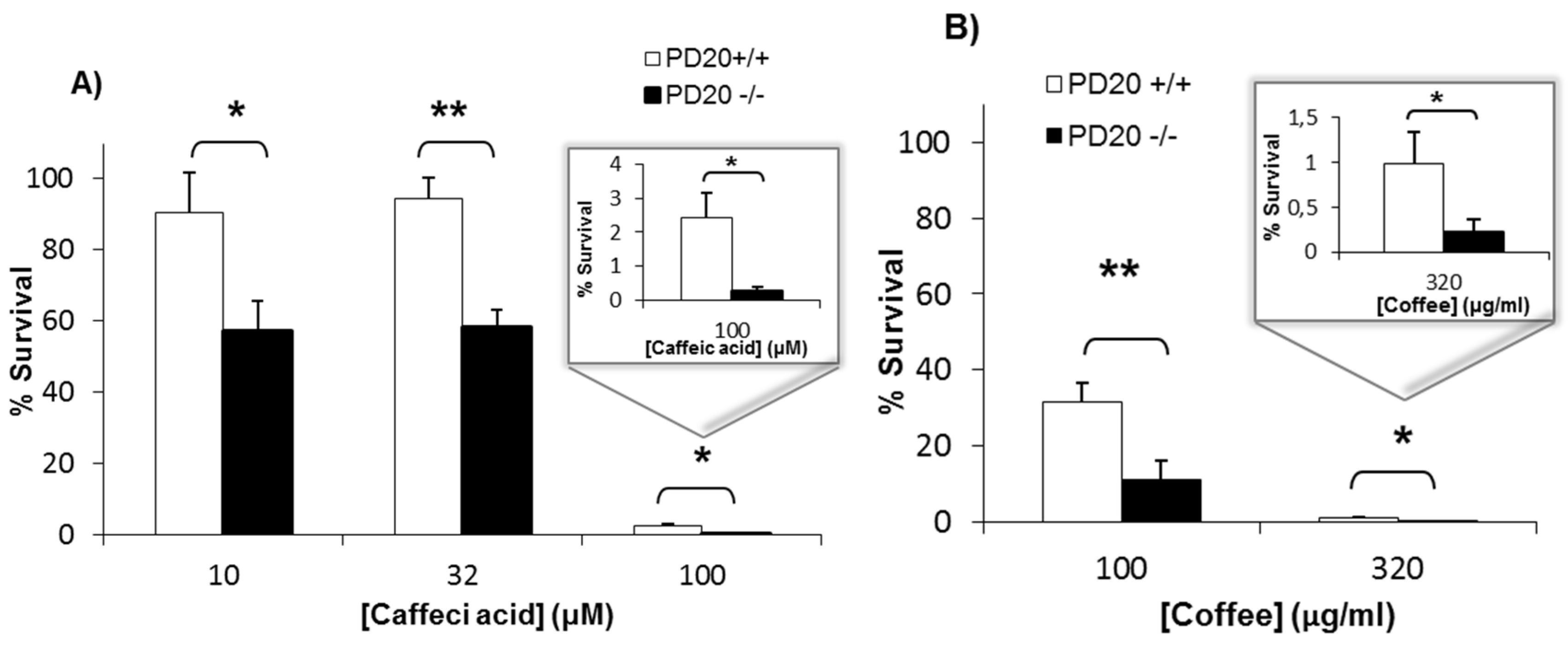 This picture illustrates How did the term cappuccino originate.
This picture illustrates How did the term cappuccino originate.
Is coffee carbohydrate
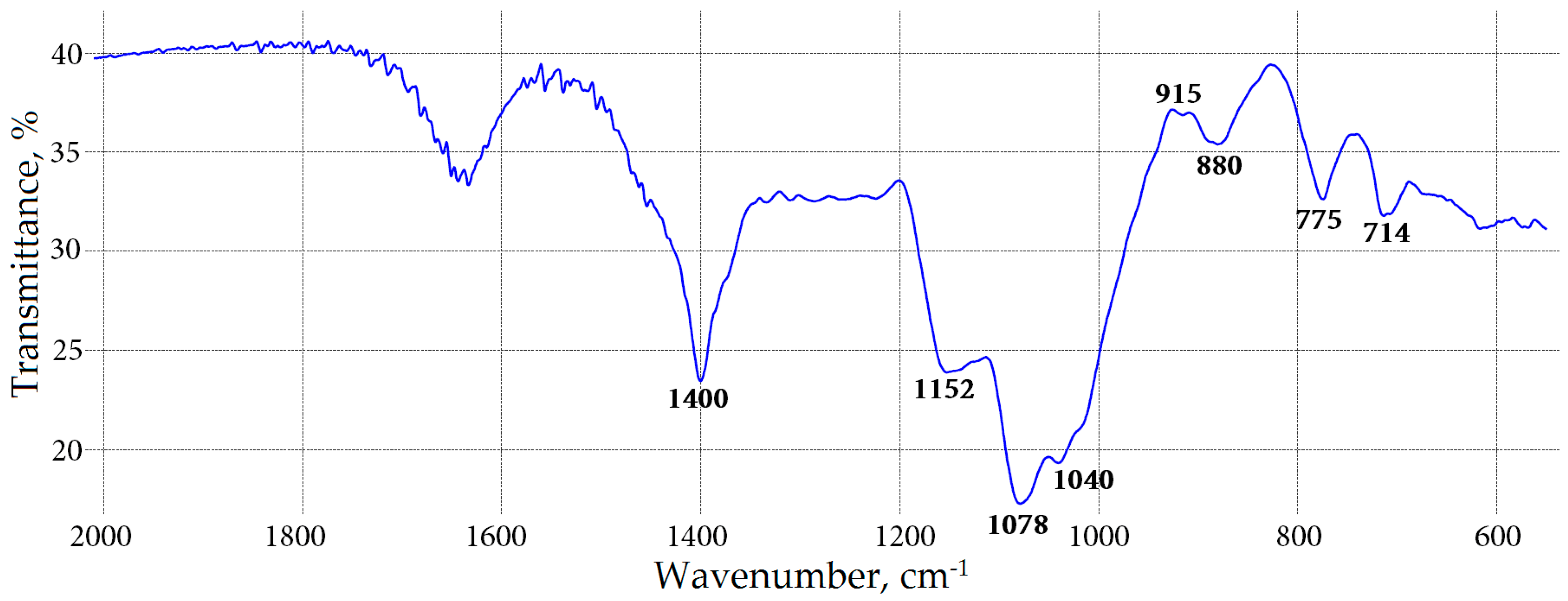 This picture shows Is coffee carbohydrate.
This picture shows Is coffee carbohydrate.
Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks
 This image representes Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks.
This image representes Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks.
Which is the best example of a phytochemical?
Total phytochemicals were highest in the green beans (GB) at 9.70 mg g −1 dry weight (DW), while roasting caused a 66% decline in the roasted beans (RB). This decline resulted more from 5–CQA and sucrose decomposition by 68% and 97%, respectively, while caffeine and trigonelline were not significantly thermally affected.
What is the phytochemical profile of coffee beans?
The current study investigates the phytochemical composition of coffee plant organs and their corresponding antioxidant capacities compared to green and roasted coffee beans.
What are the main sources of antioxidants in coffee?
Until today, coffee beans and recently leaves are the main sources of antioxidants from coffee plants. These undergo either roasting or some form of drying before utilisation. The two processes may result in significant changes in the biochemical composition and/or antioxidant capacities of the resultant beverage [ 7, 16 ].
Last Update: Oct 2021