Are you interested in finding 'heat pump essay'? You will find your answers right here.
Table of contents
- Heat pump essay in 2021
- Heat pump thermodynamics
- Heat pump how it works
- Heat pump efficiency
- Heat pump problems
- Heat pumps for dummies
- Heat pump for cooling
- Ductless heat pump
Heat pump essay in 2021
 This image illustrates heat pump essay.
This image illustrates heat pump essay.
Heat pump thermodynamics
 This image representes Heat pump thermodynamics.
This image representes Heat pump thermodynamics.
Heat pump how it works
 This image illustrates Heat pump how it works.
This image illustrates Heat pump how it works.
Heat pump efficiency
 This picture shows Heat pump efficiency.
This picture shows Heat pump efficiency.
Heat pump problems
 This picture illustrates Heat pump problems.
This picture illustrates Heat pump problems.
Heat pumps for dummies
 This picture illustrates Heat pumps for dummies.
This picture illustrates Heat pumps for dummies.
Heat pump for cooling
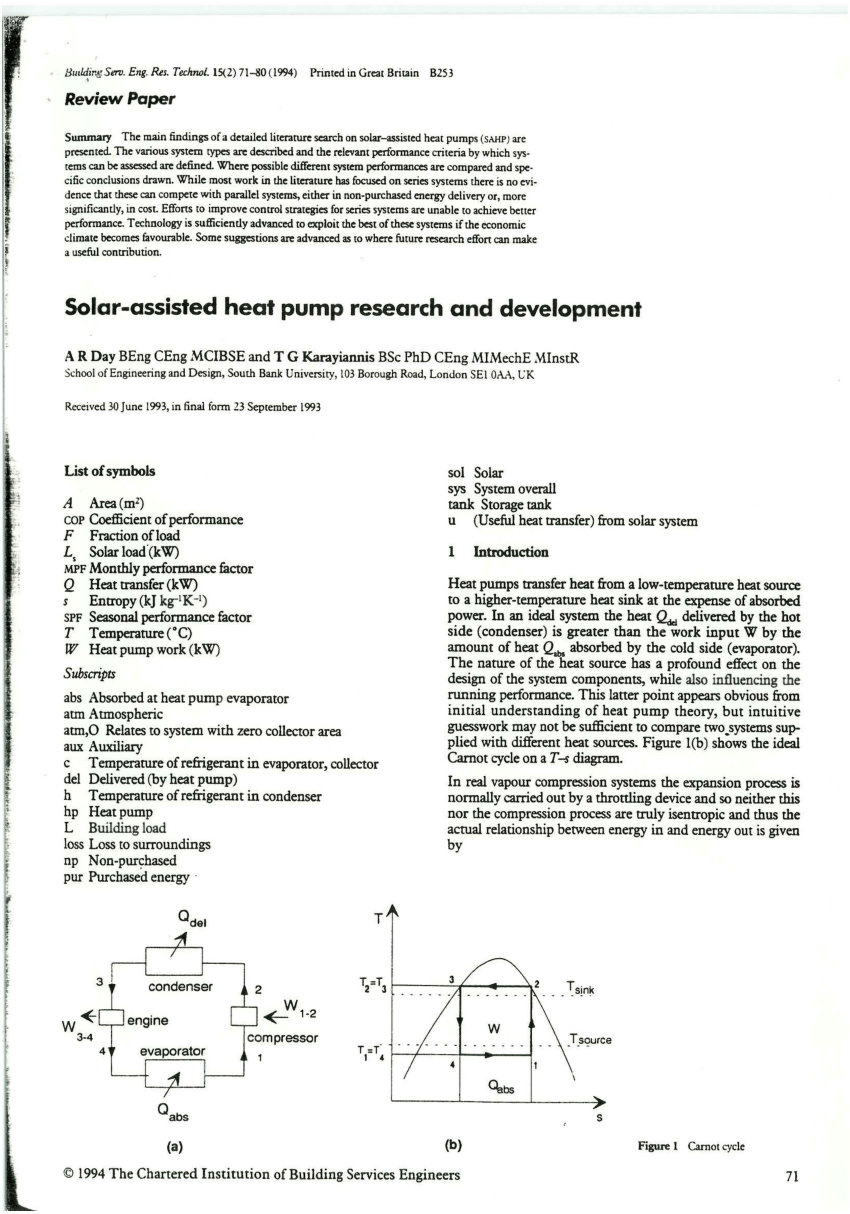 This picture shows Heat pump for cooling.
This picture shows Heat pump for cooling.
Ductless heat pump
 This picture representes Ductless heat pump.
This picture representes Ductless heat pump.
How does a heat pump work in the summer?
During summertime the heat pump can be operated in reverse, as a cooler (air conditioner). So the operation is similar, except that instead of gaining heat from the ground, the anti-freeze solution (which now acts as the cooling medium) “loses” heat to the ground.
Which is the best description of a heat pump?
An excellent reference explaining the thermodynamic details of how heat pumps work is: The Oak Ridge Heat Pump Models: I. A Steady-State Computer Design Model for Air-to-Air Heat Pumps, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, S. K. Fischer, C. K. Rice, August 1983.
How is heat energy transported in a heat pump?
To start off, let's first discuss the basics of how heat pumps work. A heat pump is a device that “transports” heat energy from one place to another place. This is the basic feature of how heat pumps work.
How to calculate the cost of a heat pump?
35,000 BTU = 10.26 kWh. To produce 10.26 kWh of heat energy, the amount of electrical energy input needed by the heat pump is 10.26/COP (e.g. for a COP = 3, the energy input is 10.26/3 = 3.4 kWh). The associated electrical cost is then EC = (10.26/COP) × (cost per kWh of electricity in your area).
Last Update: Oct 2021